Ursula von der Leyen Faces Scrutiny Amid Pfizer Vaccine Deal Allegations
Concerns arise over potential side effects and lobbying processes linked to EU vaccine procurement.
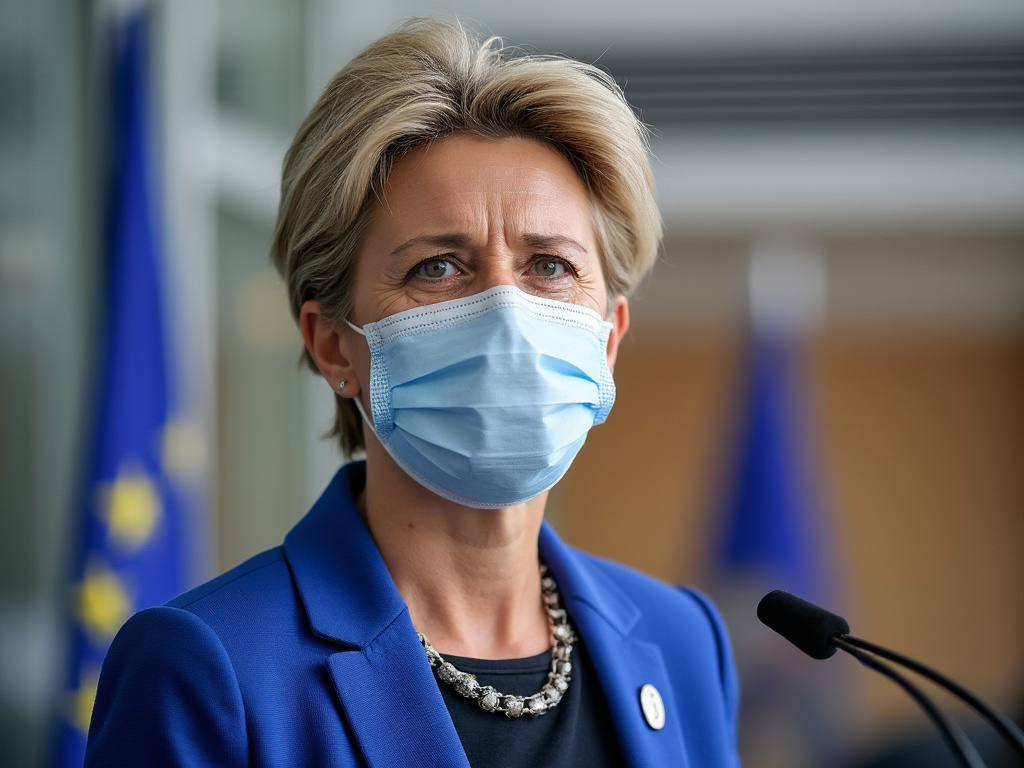
The European Commission, led by President Ursula von der Leyen, is under scrutiny regarding its procurement process for COVID-19 vaccines, particularly its arrangement with Pfizer.
Allegations have surfaced about the transparency and ethical considerations surrounding the negotiations that resulted in a substantial purchase of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines.
Critics have raised concerns about the potential long-term effects of the vaccine, although health authorities maintain that the benefits outweigh potential risks.
Additionally, reports indicate that von der Leyen’s dealings during the negotiations may have lacked sufficient oversight, prompting calls for an investigation from various stakeholders in the European Union.
As an extension of this controversy, the role of lobbying in vaccine procurement is also being examined.
The defense industries and other corporate entities have reportedly intensified their lobbying efforts to influence EU policy-making, raising questions about the integrity of the regulatory process.
This environment of increased lobbying and scrutiny reflects broader concerns regarding accountability and transparency in governmental agreements during the pandemic.
Concurrently, the European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF) is conducting investigations into several matters, including a separate inquiry into Huawei, where its director, Ville Itälä, has defended the agency’s approach to addressing concerns raised about the technology giant.
These heightened concerns and ongoing investigations highlight the complex interplay between health policy, corporate interests, and regulatory frameworks within the EU.
Allegations have surfaced about the transparency and ethical considerations surrounding the negotiations that resulted in a substantial purchase of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines.
Critics have raised concerns about the potential long-term effects of the vaccine, although health authorities maintain that the benefits outweigh potential risks.
Additionally, reports indicate that von der Leyen’s dealings during the negotiations may have lacked sufficient oversight, prompting calls for an investigation from various stakeholders in the European Union.
As an extension of this controversy, the role of lobbying in vaccine procurement is also being examined.
The defense industries and other corporate entities have reportedly intensified their lobbying efforts to influence EU policy-making, raising questions about the integrity of the regulatory process.
This environment of increased lobbying and scrutiny reflects broader concerns regarding accountability and transparency in governmental agreements during the pandemic.
Concurrently, the European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF) is conducting investigations into several matters, including a separate inquiry into Huawei, where its director, Ville Itälä, has defended the agency’s approach to addressing concerns raised about the technology giant.
These heightened concerns and ongoing investigations highlight the complex interplay between health policy, corporate interests, and regulatory frameworks within the EU.